.NET 5.0 - Basic Authentication Tutorial with Example API
Tutorial built with .NET 5.0
Other versions available:
- .NET: .NET 6.0, ASP.NET Core 3.1, 2.2
- Node: Node.js
In this tutorial we'll go through a simple example of how to implement Basic HTTP authentication in a .NET 5.0 API with C#.
The example API has just two endpoints/routes to demonstrate authenticating with basic http authentication and accessing a restricted route:
/users/authenticate- public route that accepts HTTP POST requests containing the username and password in the body. If the username and password are correct then the user details are returned./users- secure route that accepts HTTP GET requests and returns a list of all the users in the application if the HTTP Authorization header contains valid basic authentication credentials. If there are no basic auth credentials or the credentials are invalid then a 401 Unauthorized response is returned.
The tutorial project is available on GitHub at https://github.com/cornflourblue/dotnet-5-basic-authentication-api.
Tutorial Contents
- Tools required to develop .NET 5.0 applications
- Run the example API locally
- Test the .NET API with Postman
- Run an Angular app with the .NET API
- Run a Blazor app with the .NET API
- Run a React app with the .NET API
- Run a Vue.js app with the .NET API
- .NET Basic Authentication API project structure
Tools required to run the .NET 5.0 Basic Auth Example Locally
To develop and run .NET 5.0 applications locally, download and install the following:
- .NET SDK - includes the .NET runtime and command line tools
- Visual Studio Code - code editor that runs on Windows, Mac and Linux
- C# extension for Visual Studio Code - adds support to VS Code for developing .NET applications
Run the .NET Basic Authentication API Locally
- Download or clone the tutorial project code from https://github.com/cornflourblue/dotnet-5-basic-authentication-api
- Start the api by running
dotnet runfrom the command line in the project root folder (where the WebApi.csproj file is located), you should see the messageNow listening on: http://localhost:4000. Follow the instructions below to test with Postman or hook up with one of the example single page applications available (Angular, Blazor, React or Vue).
NOTE: You can also start the application in debug mode in VS Code by opening the project root folder in VS Code and pressing F5 or by selecting Debug -> Start Debugging from the top menu. Running in debug mode allows you to attach breakpoints to pause execution and step through the application code.
Test the .NET 5.0 Basic Authentication API with Postman
Postman is a great tool for testing APIs, you can download it at https://www.postman.com/downloads.
Below are instructions on how to use Postman to authenticate a user with the api, and then make an authenticated request with basic authentication credentials to retrieve a list of users from the api.
How to authenticate a user with Postman
To authenticate a user with the basic authentication api and follow these steps:
- Open a new request tab by clicking the plus (+) button at the end of the tabs.
- Change the http request method to "POST" with the dropdown selector on the left of the URL input field.
- In the URL field enter the address to the authenticate route of your local API -
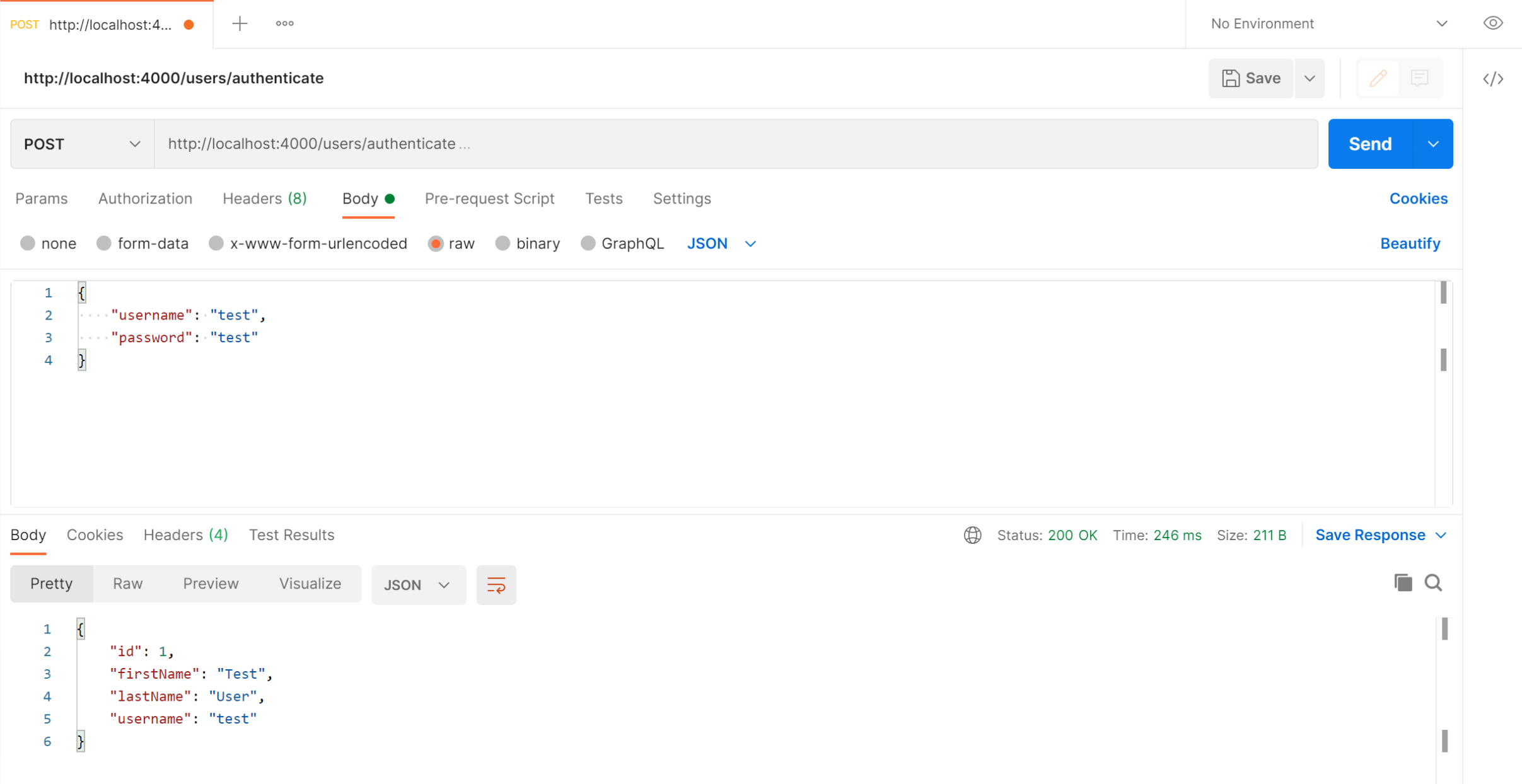
http://localhost:4000/users/authenticate. - Select the "Body" tab below the URL field, change the body type radio button to "raw", and change the format dropdown selector to "JSON (application/json)".
- Enter a JSON object containing the test username and password in the "Body" textarea:
{ "username": "test", "password": "test" } - Click the "Send" button, you should receive a "200 OK" response containing the user details in the response body, this indicates that the username and password are correct.
Here's a screenshot of Postman after the request is sent and the user has been authenticated:
How to make an authenticated request to retrieve all users
To make an authenticated request using basic authentication credentials, follow these steps:
- Open a new request tab by clicking the plus (+) button at the end of the tabs.
- Change the http request method to "GET" with the dropdown selector on the left of the URL input field.
- In the URL field enter the address to the users route of your local API -
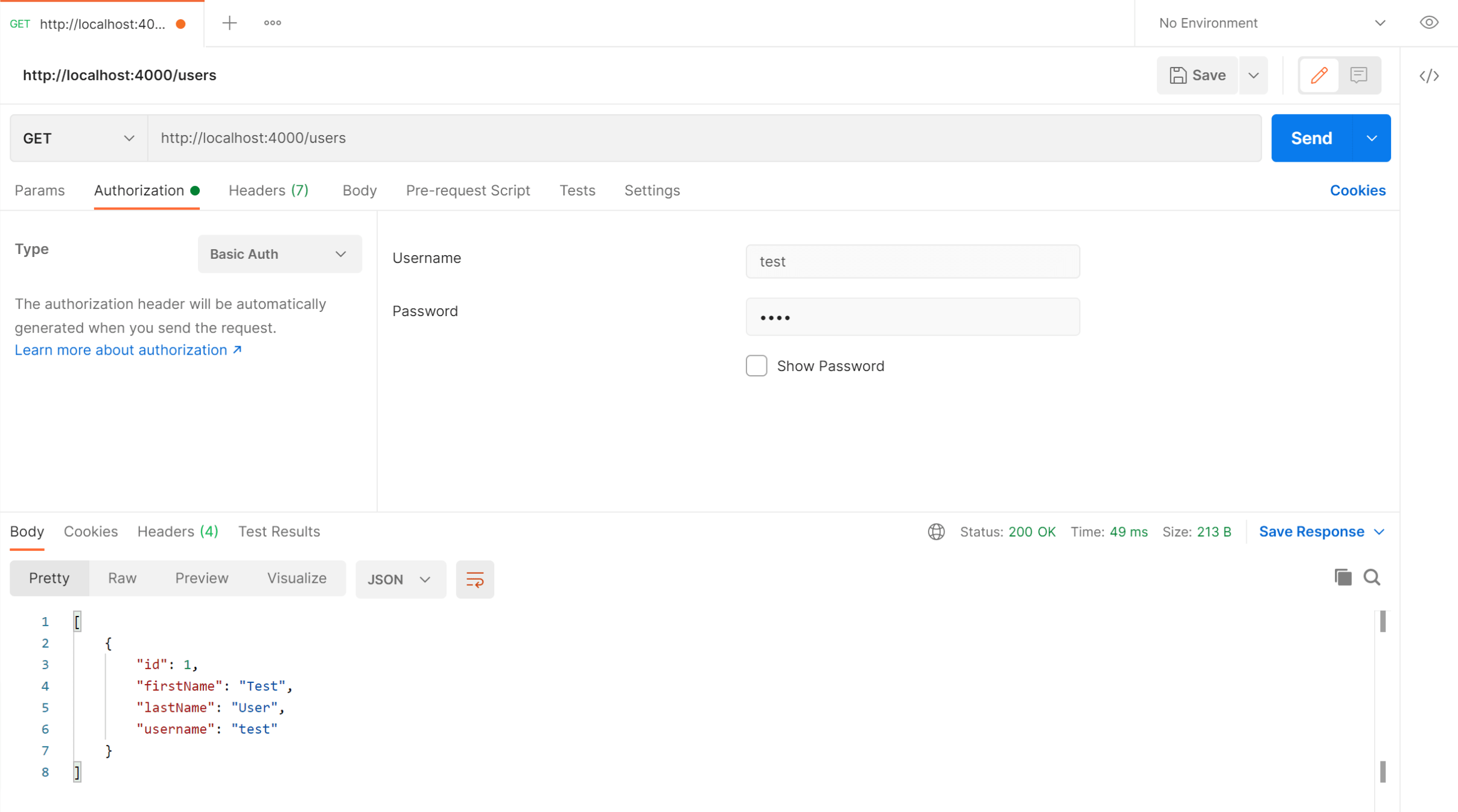
http://localhost:4000/users. - Select the "Authorization" tab below the URL field, change the type to "Basic Auth" in the type dropdown selector, enter
testinto the "Username" field andtestinto the "Password" field. - Click the "Send" button, you should receive a "200 OK" response containing a JSON array with all the user records in the system (just the one test user in the example).
Here's a screenshot of Postman after making an authenticated request to get all users:
Run an Angular client app with the .NET Basic Auth API
For full details about the example Angular application see the tutorial Angular 10 - Basic HTTP Authentication Tutorial & Example. But to get up and running quickly just follow the below steps.
- Install Node.js and npm from https://nodejs.org.
- Download or clone the Angular 8 tutorial code from https://github.com/cornflourblue/angular-10-basic-authentication-example
- Install all required npm packages by running
npm installfrom the command line in the project root folder (where the package.json is located). - Remove or comment out the line below the comment
// provider used to create fake backendlocated in the/src/app/app.module.tsfile. - Start the application by running
npm startfrom the command line in the project root folder, this will launch a browser displaying the Angular example application and it should be hooked up with the .NET 5.0 Basic Auth API that you already have running.
Run a Blazor WebAssembly (WASM) client app with the .NET Basic Auth API
For full details about the example Blazor application see the post Blazor WebAssembly - Basic HTTP Authentication Tutorial & Example. But to get up and running quickly just follow the below steps.
- Download or clone the tutorial project code from https://github.com/cornflourblue/blazor-webassembly-basic-authentication-example
- Change the
"fakeBackend"setting to"false"in the/wwwroot/appsettings.jsonfile. - Start the app by running
dotnet runfrom the command line in the project root folder (where the BlazorApp.csproj file is located) - Open a new browser tab and navigate to the URL
http://localhost:5000, the Blazor app should be hooked up with the .NET 5.0 Basic Auth API that you already have running.
NOTE: To enable hot reloading during development so the Blazor app automatically restarts when a file is changed, start the app with the command dotnet watch run.
Run a React client app with the .NET Basic Auth API
For full details about the example React application see the post React - Basic HTTP Authentication Tutorial & Example. But to get up and running quickly just follow the below steps.
- Install Node.js and npm from https://nodejs.org.
- Download or clone the React tutorial code from https://github.com/cornflourblue/react-basic-authentication-example
- Install all required npm packages by running
npm installfrom the command line in the project root folder (where the package.json is located). - Remove or comment out the 2 lines below the comment
// setup fake backendlocated in the/src/index.jsxfile. - Start the application by running
npm startfrom the command line in the project root folder, this will launch a browser displaying the React example application and it should be hooked up with the .NET 5.0 Basic Auth API that you already have running.
Run a Vue.js client app with the .NET Basic Auth API
For full details about the example Vue.js application see the post Vue.js - Basic HTTP Authentication Tutorial & Example. But to get up and running quickly just follow the below steps.
- Install Node.js and npm from https://nodejs.org.
- Download or clone the VueJS tutorial code from https://github.com/cornflourblue/vue-basic-authentication-example
- Install all required npm packages by running
npm installfrom the command line in the project root folder (where the package.json is located). - Remove or comment out the 2 lines below the comment
// setup fake backendlocated in the/src/index.jsfile. - Start the application by running
npm startfrom the command line in the project root folder, this will launch a browser displaying the VueJS example application and it should be hooked up with the .NET 5.0 Basic Auth API that you already have running.
.NET Basic Authentication API Project Structure
The tutorial project is organised into the following folders:
Controllers - define the end points / routes for the web api, controllers are the entry point into the web api from client applications via http requests.
Models - represent request and response models for controller methods, request models define the parameters for incoming requests, and response models can be used to define what data is returned.
Services - contain business logic, validation and data access code.
Entities - represent the application data.
Helpers - anything that doesn't fit into the above folders.
Click any of the below links to jump down to a description of each file along with its code:
- Controllers
- Entities
- Helpers
- Models
- Services
- appsettings.Development.json
- appsettings.json
- omnisharp.json
- Program.cs
- Startup.cs
- WebApi.csproj
Users Controller
The .NET users controller defines and handles all routes / endpoints for the api that relate to users, this includes authentication and standard CRUD operations. Within each route the controller calls the user service to perform the action required, this enables the controller to stay 'lean' and completely separated from the business logic and data access code.
The controller actions are secured with basic authentication using the [Authorize] attribute, with the exception of the Authenticate method which allows public access by overriding the [Authorize] attribute on the controller with the [AllowAnonymous] attribute on the action method. I chose this approach so any new action methods added to the controller will be secure by default unless explicitly made public.
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Authorization;
using WebApi.Services;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using WebApi.Models;
namespace WebApi.Controllers
{
[Authorize]
[ApiController]
[Route("[controller]")]
public class UsersController : ControllerBase
{
private IUserService _userService;
public UsersController(IUserService userService)
{
_userService = userService;
}
[AllowAnonymous]
[HttpPost("authenticate")]
public async Task<IActionResult> Authenticate([FromBody]AuthenticateModel model)
{
var user = await _userService.Authenticate(model.Username, model.Password);
if (user == null)
return BadRequest(new { message = "Username or password is incorrect" });
return Ok(user);
}
[HttpGet]
public async Task<IActionResult> GetAll()
{
var users = await _userService.GetAll();
return Ok(users);
}
}
}
User Entity
The user entity class represents the data for a user in the application. Entity classes are used to pass data between different parts of the application (e.g. between services and controllers) and can be used to return http response data from controller action methods.
The [JsonIgnore] attribute prevents the password property from being serialized and returned with user data in api responses.
using System.Text.Json.Serialization;
namespace WebApi.Entities
{
public class User
{
public int Id { get; set; }
public string FirstName { get; set; }
public string LastName { get; set; }
public string Username { get; set; }
[JsonIgnore]
public string Password { get; set; }
}
}
Basic Authentication Handler
The basic authentication handler is .NET middleware that handles request authentication by inheriting from the .NET AuthenticationHandler base class and overriding the HandleAuthenticateAsync() method.
Basic authentication logic is implemented in the HandleAuthenticateAsync() method by verifying the username and password received in the HTTP Authorization header, verification is done by calling _userService.Authenticate(username, password). On successful authentication the method returns AuthenticateResult.Success(ticket) which makes the request authenticated and sets the HttpContext.User to the currently logged in user.
The HandleChallengeAsync method is overridden to append the WWW-Authenticate response header when basic authentication fails. The WWW-Authenticate header triggers a username/password popup in browsers.
The basic authentication middleware is configured in the application inside the ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services) method in the application Startup file below.
using System;
using System.Net.Http.Headers;
using System.Security.Claims;
using System.Text;
using System.Text.Encodings.Web;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Authentication;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Authorization;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Http;
using Microsoft.Extensions.Logging;
using Microsoft.Extensions.Options;
using WebApi.Entities;
using WebApi.Services;
namespace WebApi.Helpers
{
public class BasicAuthenticationHandler : AuthenticationHandler<AuthenticationSchemeOptions>
{
private readonly IUserService _userService;
public BasicAuthenticationHandler(
IOptionsMonitor<AuthenticationSchemeOptions> options,
ILoggerFactory logger,
UrlEncoder encoder,
ISystemClock clock,
IUserService userService)
: base(options, logger, encoder, clock)
{
_userService = userService;
}
protected override async Task<AuthenticateResult> HandleAuthenticateAsync()
{
// skip authentication if endpoint has [AllowAnonymous] attribute
var endpoint = Context.GetEndpoint();
if (endpoint?.Metadata?.GetMetadata<IAllowAnonymous>() != null)
return AuthenticateResult.NoResult();
if (!Request.Headers.ContainsKey("Authorization"))
return AuthenticateResult.Fail("Missing Authorization Header");
User user = null;
try
{
var authHeader = AuthenticationHeaderValue.Parse(Request.Headers["Authorization"]);
var credentialBytes = Convert.FromBase64String(authHeader.Parameter);
var credentials = Encoding.UTF8.GetString(credentialBytes).Split(new[] { ':' }, 2);
var username = credentials[0];
var password = credentials[1];
user = await _userService.Authenticate(username, password);
}
catch
{
return AuthenticateResult.Fail("Invalid Authorization Header");
}
if (user == null)
return AuthenticateResult.Fail("Invalid Username or Password");
var claims = new[] {
new Claim(ClaimTypes.NameIdentifier, user.Id.ToString()),
new Claim(ClaimTypes.Name, user.Username),
};
var identity = new ClaimsIdentity(claims, Scheme.Name);
var principal = new ClaimsPrincipal(identity);
var ticket = new AuthenticationTicket(principal, Scheme.Name);
return AuthenticateResult.Success(ticket);
}
protected override Task HandleChallengeAsync(AuthenticationProperties properties)
{
Response.Headers["WWW-Authenticate"] = "Basic realm=\"\", charset=\"UTF-8\"";
return base.HandleChallengeAsync(properties);
}
}
}
Authenticate Model
The authenticate model defines the parameters for incoming requests to the /users/authenticate route of the api, because it is set as the parameter to the Authenticate method of the UsersController. When an HTTP POST request is received to the route, the data from the body is bound to an instance of the AuthenticateModel, validated and passed to the method.
.NET Data Annotations are used to automatically handle model validation, the [Required] attribute sets both the username and password as required fields so if either are missing a validation error message is returned from the api.
using System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations;
namespace WebApi.Models
{
public class AuthenticateModel
{
[Required]
public string Username { get; set; }
[Required]
public string Password { get; set; }
}
}
User Service
The user service contains a method for authenticating user credentials, and a method for getting all users in the application.
I hardcoded the array of users in the example to keep it focused on basic http authentication, in a production application it is recommended to store user records in a database with hashed passwords. For an extended example that includes support for user registration and stores data with Entity Framework check out .NET 5.0 - Simple API for Authentication, Registration and User Management.
The top of the file contains an interface that defines the user service, below that is the concrete user service class that implements the interface.
On successful authentication the Authenticate method returns the user details, the client application should then include the base64 encoded user credentials in the HTTP Authorization header of subsequent api requests to access secure endpoints.
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using WebApi.Entities;
namespace WebApi.Services
{
public interface IUserService
{
Task<User> Authenticate(string username, string password);
Task<IEnumerable<User>> GetAll();
}
public class UserService : IUserService
{
// users hardcoded for simplicity, store in a db with hashed passwords in production applications
private List<User> _users = new List<User>
{
new User { Id = 1, FirstName = "Test", LastName = "User", Username = "test", Password = "test" }
};
public async Task<User> Authenticate(string username, string password)
{
// wrapped in "await Task.Run" to mimic fetching user from a db
var user = await Task.Run(() => _users.SingleOrDefault(x => x.Username == username && x.Password == password));
// return null if user not found
if (user == null)
return null;
// authentication successful so return user details
return user;
}
public async Task<IEnumerable<User>> GetAll()
{
// wrapped in "await Task.Run" to mimic fetching users from a db
return await Task.Run(() => _users);
}
}
}
.NET App Settings (Development)
Configuration file with application settings that are specific to the development environment.
{
"Logging": {
"LogLevel": {
"Default": "Debug",
"System": "Information",
"Microsoft": "Information"
}
}
}
.NET App Settings
Root configuration file containing application settings for all environments.
{
"Logging": {
"LogLevel": {
"Default": "Information",
"Microsoft": "Warning",
"Microsoft.Hosting.Lifetime": "Information"
}
},
"AllowedHosts": "*"
}
OmniSharp Config
This file contains configuration options for the C# extension in VS Code. The useBundledOnly option tells the C# extension to use the bundled version of MSBuild instead of the global version to prevent errors if you have an older version of MSBuild installed globally (e.g. as part of Visual Studio).
{
"msbuild": {
"useBundledOnly": true
}
}
Program
The program class is a console app that is the main entry point to start the application, it configures and launches the web api host and web server using an instance of IHostBuilder. .NET applications require a host in which to execute.
Kestrel is the web server used in the example, it's a new cross-platform web server for .NET that's included in new project templates by default. Kestrel is fine to use on it's own for internal applications and development, but for public facing websites and applications it should sit behind a more mature reverse proxy server (IIS, Apache, Nginx etc) that will receive HTTP requests from the internet and forward them to Kestrel after initial handling and security checks.
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Hosting;
using Microsoft.Extensions.Hosting;
namespace WebApi
{
public class Program
{
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
CreateHostBuilder(args).Build().Run();
}
public static IHostBuilder CreateHostBuilder(string[] args) =>
Host.CreateDefaultBuilder(args)
.ConfigureWebHostDefaults(webBuilder =>
{
webBuilder.UseStartup<Startup>()
.UseUrls("http://localhost:4000");
});
}
}
Startup
The startup class configures the request pipeline of the application and how all requests are handled.
The basic authentication handler is configured for the application in the ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services) method.
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Builder;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Hosting;
using Microsoft.Extensions.Configuration;
using Microsoft.Extensions.DependencyInjection;
using WebApi.Helpers;
using WebApi.Services;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Authentication;
namespace WebApi
{
public class Startup
{
public Startup(IConfiguration configuration)
{
Configuration = configuration;
}
public IConfiguration Configuration { get; }
// This method gets called by the runtime. Use this method to add services to the container.
public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services)
{
services.AddCors();
services.AddControllers();
// configure basic authentication
services.AddAuthentication("BasicAuthentication")
.AddScheme<AuthenticationSchemeOptions, BasicAuthenticationHandler>("BasicAuthentication", null);
// configure DI for application services
services.AddScoped<IUserService, UserService>();
}
// This method gets called by the runtime. Use this method to configure the HTTP request pipeline.
public void Configure(IApplicationBuilder app, IWebHostEnvironment env)
{
app.UseRouting();
// global cors policy
app.UseCors(x => x
.AllowAnyOrigin()
.AllowAnyMethod()
.AllowAnyHeader());
app.UseAuthentication();
app.UseAuthorization();
app.UseEndpoints(endpoints => endpoints.MapControllers());
}
}
}
.NET Basic Auth API csproj
The csproj (C# project) is an MSBuild based file that contains target framework and NuGet package dependency information for the application.
<Project Sdk="Microsoft.NET.Sdk.Web">
<PropertyGroup>
<TargetFramework>net5.0</TargetFramework>
</PropertyGroup>
</Project>
Need Some .NET Help?
Search fiverr for freelance .NET developers.
Follow me for updates
When I'm not coding...
Me and Tina are on a motorcycle adventure around Australia.
Come along for the ride!
